Keywords AI
Fine-Tuning LLMs with Custom Datasets
Previously, we discussed methods to prevent LLM hallucinations, highlighting three main strategies: advanced prompting, retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), and fine-tuning. In this blog, we'll focus on fine-tuning large language models (LLMs) and guide you through creating a custom dataset for this purpose.
What is LLM fine-tuning?
Fine-tuning large language models (LLMs) involves training a pre-existing model, like GPT-3, on a smaller, specific dataset to make it better at specialized tasks. This process uses the model's existing knowledge, saving time and resources compared to training a model from scratch.
By fine-tuning, we can adapt a general model to specific needs. For example, GPT-3 can be fine-tuned with medical reports to help it understand and generate accurate medical content. This makes the model more useful for particular applications, improving its performance in specialized areas while retaining its broad language skills.
When to fine-tune
Fine-tuning is particularly useful in several situations:
- Specializing in a Specific Domain: When you need the model to handle specialized content, like legal documents, medical reports, or technical jargon, fine-tuning helps the model become proficient in that area.
- Improving Task Performance: Fine-tuning the model with relevant data improves performance and output quality if you're working on a specific task, such as generating creative writing or translating languages.
- Customizing Outputs: Fine-tuning allows you to adjust the model’s tone, style, or level of detail to match your specific needs, such as creating a distinct voice for content or ensuring appropriate formality in communication.
- Adapting to Changing Data: When the data distribution shifts over time, fine-tuning helps the model stay accurate and relevant, ensuring it performs well with new data.
- Enhancing Privacy and Fairness: Fine-tuning can focus on improving privacy and security for applications that handle sensitive information. Additionally, it can help mitigate biases by using balanced datasets to train the model, promoting fairness.
In essence, fine-tuning is beneficial when you must tailor a general model to meet specific requirements, enhance its task performance, customize its outputs, adapt to new data, or improve its handling of privacy and fairness issues.
Steps of Fine-Tuning
There are key steps for developers to fine-tune a Large Language Model (LLM):
- Select a Pre-Trained Model: Previously, GPT-3 was the primary choice for fine-tuning due to its performance and limited alternatives. However, as of mid-2024, numerous models are available, each with its own strengths. Options now include Mistral-7B, Cohere Command-R, Meta LLaMA 2, and GPT-4.
- Prepare your custom dataset: Gather a dataset relevant to your specific task or domain. Once you have the raw data, preprocess it by cleaning and organizing it. This includes splitting the dataset into training and testing sets to ensure the model can learn effectively and be appropriately evaluated.
- Fine-tuning: Choose a fine-tuning platform to train your model or opt to train it in-house, depending on your resources and requirements.
- Validation: Fine-tuning a model is an ongoing process. Continuously monitor its performance using accuracy, loss, and precision metrics. Adjust parameters as needed to optimize the model for your specific task, ensuring it meets your desired performance standards.
Methods for fine-tuning LLMs
Fine-tuning a Large Language Model (LLM) involves a supervised learning process where labeled examples adjust the model’s weights to enhance its proficiency in specific tasks. Here are some notable techniques used in fine-tuning:
Full Fine-Tuning (Instruction Fine-Tuning)
Instruction fine-tuning, or full fine-tuning, updates all the model's weights to improve its performance across various tasks. This technique involves training the model on examples that guide its responses to specific queries. The dataset used is tailored to the task at hand, such as summarization or translation. Full fine-tuning creates a new version of the model with enhanced capabilities, but it requires significant memory and computational resources, similar to pre-training, to store and process gradients, optimizers, and other components during training.
Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT)
Parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) is more resource-efficient than full fine-tuning. It addresses the challenge of high memory and computational requirements by updating only a subset of the model's parameters and "freezing" the rest. This reduces the number of trainable parameters, making memory requirements more manageable and preventing catastrophic forgetting, where the model loses previously learned information. PEFT maintains the original LLM weights, ensuring the retention of general knowledge while fine-tuning for specific tasks. Techniques like Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) and Quantized LoRA (QLoRA) are popular and effective methods within PEFT, significantly reducing the number of trainable parameters and optimizing the fine-tuning process.
How to have your own golden dataset?
Having the right dataset is crucial for effective fine-tuning. However, selecting the most appropriate one can be challenging. Here are two methods to obtain a suitable dataset:
Pick an existing dataset
There are numerous existing datasets available for developers to use in fine-tuning models. You can choose one based on your specific use case. Here are some high-quality examples:
Customize a Dataset Based on Your Specific Needs
Sometimes, existing datasets won’t meet your specific requirements, or you may want to transition from using public models to a custom model for tasks like developing a specialized chatbot for your website or a unique coding assistant for your AI product. In such cases, you need to create a customized dataset using your own data. This involves collecting and labeling relevant data for your use case, ensuring it aligns perfectly with your tasks and objectives.
Example
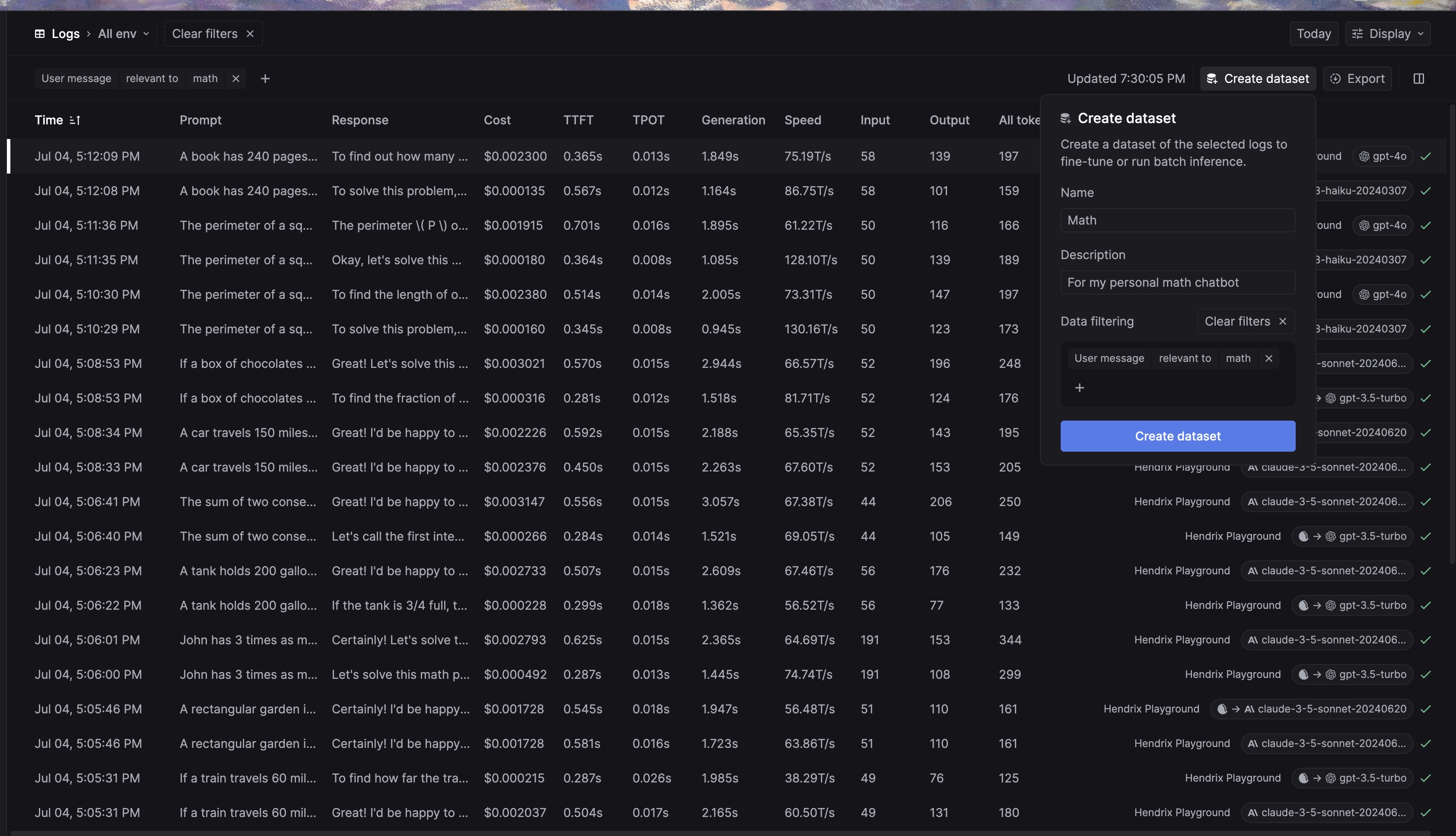
You can use Keywords AI to collect and analyze your LLM logs, tagging them for easy filtering. Once your request logs are recorded, you can edit them to create a dataset for fine-tuning models.
For example, you can search for logs related to math and gather them into a new dataset. You can then edit and delete logs as needed to ensure your dataset is optimized for the best performance.